Diabetic retinopathy is a serious eye condition that affects individuals with diabetes, leading to vision impairment and potentially blindness if left untreated. As one of the most common complications of diabetes, it is crucial to understand its causes, symptoms, and preventive measures. This blog delves into the details of diabetic retinopathy and offers strategies for managing and preventing this condition.
What is Diabetic Retinopathy?
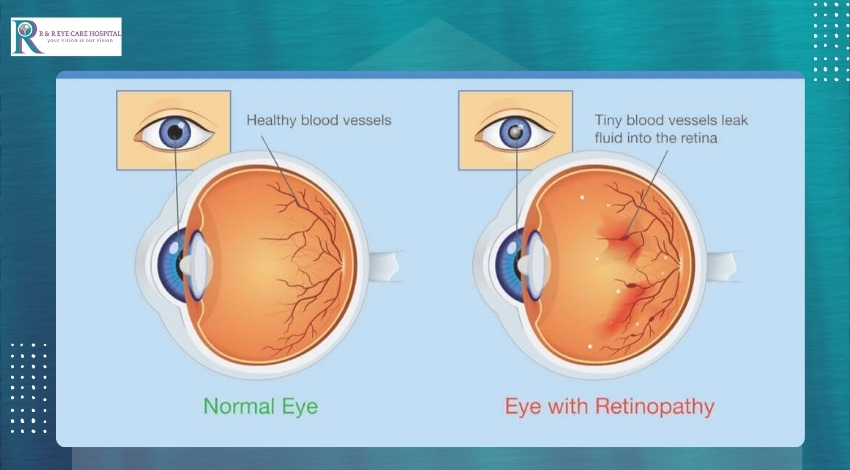
Diabetic retinopathy is a condition where high blood sugar levels cause damage to the blood vessels in the retina, the light-sensitive tissue at the back of the eye. The retina is essential for vision, as it converts light into signals that are sent to the brain. When blood vessels in the retina are damaged, they can leak fluid or hemorrhage, leading to vision problems.
Stages of Diabetic Retinopathy
Diabetic retinopathy progresses through several stages:
Mild Non-Proliferative Retinopathy:
Early stage where small areas of balloon-like swelling (microaneurysms) occur in the blood vessels of the retina.
Moderate Non-Proliferative Retinopathy:
Progression from mild to moderate, with some blood vessels becoming blocked.
Severe Non-Proliferative Retinopathy:
More blood vessels are blocked, depriving areas of the retina of their blood supply. This signals the retina to grow new blood vessels.
Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy:
The most advanced stage, where new blood vessels grow abnormally and can bleed into the vitreous, the gel-like substance inside the eye. This can cause severe vision loss or blindness.
Causes and Risk Factors
The primary cause of diabetic retinopathy is prolonged high blood sugar levels. Several factors can increase the risk, including:
Duration of Diabetes: The longer you have diabetes, the higher your risk of developing retinopathy.
Poor Blood Sugar Control: Consistently high blood sugar levels increase the risk.
High Blood Pressure: Elevated blood pressure can exacerbate damage to retinal blood vessels.
High Cholesterol: High cholesterol levels can also contribute to blood vessel damage.
Pregnancy: Pregnancy can worsen diabetic retinopathy in women with diabetes.
Tobacco Use: Smoking can increase the risk of developing retinopathy.
Symptoms of Diabetic Retinopathy
In the early stages, diabetic retinopathy may not cause any symptoms. As the condition progresses, symptoms can include:
Blurred vision.
Floaters or dark spots in your vision.
Difficulty seeing at night.
Vision loss or changes in vision.
It is essential to have regular eye exams, as diabetic retinopathy can be detected through a comprehensive dilated eye exam before symptoms become noticeable.
Preventing Diabetic Retinopathy
While diabetic retinopathy cannot always be prevented, several steps can significantly reduce the risk:
Manage Blood Sugar Levels
Maintaining good blood sugar control is crucial. Monitor your blood sugar levels regularly and follow your doctor’s recommendations for diet, exercise, and medication.
Regular Eye Exams
Schedule comprehensive dilated eye exams at least once a year. Early detection and treatment can prevent or delay vision loss.
Control Blood Pressure and Cholesterol
Keep your blood pressure and cholesterol levels within the target range. Medications, a healthy diet, and regular exercise can help manage these conditions.
Healthy Lifestyle Choices
Adopt a healthy lifestyle to support overall well-being. This includes eating a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins. Avoid smoking and limit alcohol consumption.
Regular Exercise
Engage in regular physical activity to help control blood sugar levels and improve cardiovascular health. Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate exercise most days of the week.
Treatments for Diabetic Retinopathy
If you are diagnosed with diabetic retinopathy, several treatment options are available to manage the condition and prevent further vision loss:
-
Laser Treatment (Photocoagulation)
Laser treatment can seal or shrink abnormal blood vessels and reduce fluid leakage. It is often used in the early stages of proliferative diabetic retinopathy.
-
Intravitreal Injections
Medications injected into the vitreous can help reduce inflammation, slow the growth of abnormal blood vessels, and decrease fluid leakage. These injections may need to be repeated over time.
-
Vitrectomy
Vitrectomy is a surgical procedure that removes the vitreous gel and blood from the eye. It is used for more advanced cases of diabetic retinopathy where there is significant bleeding or scarring.
Living with Diabetic Retinopathy
Managing diabetic retinopathy requires a proactive approach to your overall health. Regular monitoring of your condition, adherence to treatment plans, and lifestyle modifications are essential. Work closely with your healthcare team, including your primary care physician, endocrinologist, and ophthalmologist, to develop a comprehensive care plan.
Conclusion
Diabetic retinopathy is a serious but manageable condition. By understanding its causes, recognizing symptoms, and taking preventive measures, you can protect your vision and maintain a good quality of life. Prioritize regular eye exams, manage your blood sugar levels, and adopt a healthy lifestyle to reduce your risk. Early detection and treatment are key to preserving your vision and preventing complications associated with diabetic retinopathy.


Leave A Comment